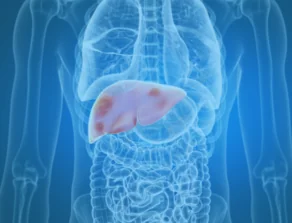
Liver Cancer
About Liver Cancer
Liver cancer is the fifth most common cancer in men and the ninth most common cancer in women worldwide. The incidence rate of liver cancer is larger in developing countries. In the U.S., the rate increases in women by 2% per year and for men, the rate has stabilized.
Liver Cancer Key Facts
- An estimated 41,630 new cases of liver cancer will be diagnosed in the U.S. in 2024, with 29,840 deaths expected to result from the diagnosis.
- For the 43% of people who are diagnosed with liver cancer at localized-stage, the five-year survival rate is 37%.
- For those people diagnosed with liver cancer at regional stages, the five-year survival rate drops to 14%.
- Liver cancer is approximately three times as likely to occur in men than in women.
- The liver is a common place where cancer spreads. Colorectal, breast, esophageal, stomach, pancreatic, kidney, lung and melanoma skin cancers are the most common sources of cancer that metastasize to the liver.
- Approximately 70% of liver cancer cases in the US could potentially be prevented through elimination of risk factors, the most important including excess body weight; type 2 diabetes; infection with hepatitis B virus (HBV) and/or hepatitis C (HCV), heavy alcohol consumption and tobacco smoking.
Source: American Cancer Society’s Cancer Facts & Figures 2024 and GLOBOCAN, 2020
- Get the hepatitis B (HBV) vaccine
- Screening and testing for chronic HBV and HCV infection
- Get treatment for chronic hepatitis B in infection
- Reduce the exposure to aflatoxin B1
- Limit alcohol usage
- Limit tobacco usage
- Healthy lifestyle
- Limit exposure to cancer-causing chemicals
- Treat diseases that increase liver cancer risk
Resource: Can Liver Cancer Be Prevented? | American Cancer Society
A symptom is a change in the body that a person can see and/or feel. A sign is a change that the doctor sees during an examination or on a laboratory test result. If you have any of the symptoms below, it does not mean you have cancer but you should see your doctor or health care professional so that the cause can be found and treated, if needed.
- Weight loss (without trying)
- Loss of appetite
- Feeling very full after a small meal
- Nausea or vomiting
- An enlarged liver, felt as fullness under the ribs on the right side
- An enlarged spleen, felt as fullness under the ribs on the left side
- Pain in the abdomen (belly) or near the right shoulder blade
- Swelling or fluid build-up in the abdomen (belly)
- Itching
- Yellowing of the skin and eyes (jaundice)
Source: American Cancer Society 2024
- Sex – more common in men
- Race/Ethnicity – Asian Americans and Pacific Islanders have the highest rates of liver cancer
- Chronic viral hepatitis – hepatitis B (HBV) or hepatitis C (HCV)
- Cirrhosis
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
- Primary biliary cirrhosis
- Inherited metabolic disease
- Heavy alcohol usage
- Tobacco usage
- Obesity
- Type 2 diabetes
- Certain rare diseases, such as
- Tyrosinemia
- Alpha1-antitrypsin deficiency
- Porphyria cutanea tarda
- Glycogen storage diseases
- Wilson disease
- Aflatoxins
- Vinyl chloride and thorium dioxide (Thorotrast)
- Anabolic steroid
- Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) – A condition that can cause cirrhosis that may lead to liver cancer
Resource:
Liver Cancer Risk Factors | Risk of Liver Cancer | American Cancer Society
Liver Cancer Causes, Risk Factors, and Prevention – NCI
NFCR-Supported Researchers Working on Liver Cancer
Yung-Chi Cheng, Ph.D.
Yale University
Ronald A. DePinho, M.D.
University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center
Paul Fisher, M.Ph., Ph.D.
Virginia Commonwealth University School of Medicine
Webster K. Cavenee, Ph.D.
Ludwig Institute for Cancer Research

Liver Cancer Awareness Month is recognized in October.
Sign-up to Receive NFCR Emails
Be the first to learn about breakthroughs in cancer research and follow NFCR’s progress on making cures possible!
A world without cancer is possible. Help us turn lab breakthroughs into life-saving realities.

5.7 Million+
Donors who have fueled NFCR’s mission

$420 Million+
Invested in high-impact research & programs
36+ Labs & Hundreds of
Nobel Laureates & Key Scientists received NFCR funding, driving breakthrough research