Head and Neck Cancer Awareness Month
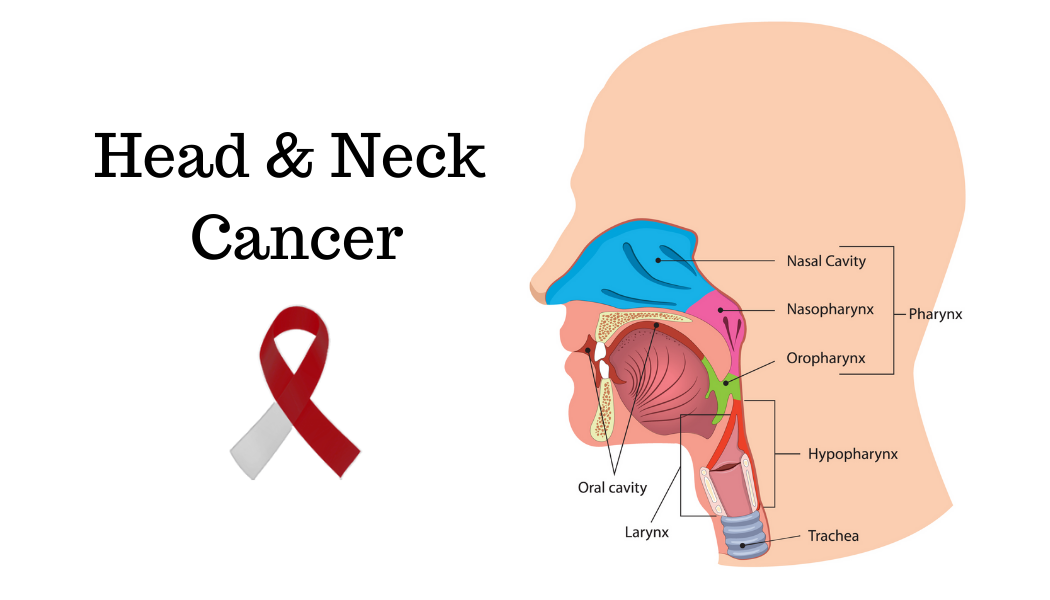 Though only making up 4% of cancer diagnoses in the United States, it is estimated that head and neck cancer will take the lives of approximately 14,620 Americans this year alone. Head and neck cancer refer to cancers in the oral cavity, pharynx, larynx, sinuses and nasal cavity, and salivary glands. These cancers are often accompanied by symptoms that are uncomfortable and disruptive to everyday life, such as difficulty chewing, swallowing, breathing, or moving one’s jaw. Luckily, many cases of head and neck cancer are preventable and current treatment can often remove the tumor without many complications.
Though only making up 4% of cancer diagnoses in the United States, it is estimated that head and neck cancer will take the lives of approximately 14,620 Americans this year alone. Head and neck cancer refer to cancers in the oral cavity, pharynx, larynx, sinuses and nasal cavity, and salivary glands. These cancers are often accompanied by symptoms that are uncomfortable and disruptive to everyday life, such as difficulty chewing, swallowing, breathing, or moving one’s jaw. Luckily, many cases of head and neck cancer are preventable and current treatment can often remove the tumor without many complications.
Prevention
The majority of head and neck cancer cases are preventable with certain lifestyle modifications. Some risk factors, such as gender and age, are uncontrollable but work in conjunction with modifiable risk factors. Men, for example, are two to three times more likely than women to develop head and neck cancer. It is also more common to see such cancers in people over the age of 40. To greatly reduce the chances of developing head and neck cancer, individuals should consider:
- Eliminating tobacco use
Like many health-related concerns, quitting or reducing tobacco use can greatly reduce one’s risk of developing head and neck cancer. Tobacco, including cigarettes, cigars, pipes, smokeless tobacco and secondhand smoke, is the single largest risk factor associated with this type of cancer. In fact, 85% of head and neck cancers are attributed to tobacco use. While quitting use altogether is the best way to protect oneself from head and neck cancer, reducing the amount used may positively affect one’s chance of recovery.
- Reducing alcohol consumption
Frequent and heavy alcohol consumption is a major risk factor associated with head and neck cancer. Reducing alcohol consumption should be done over a prolonged period of time, as the risk of developing cancer reduces slowly over time as one reduces or stops consumption.
- Minimizing sun exposure and be UV smart
Skin cancer and cancer around the lip area are most often caused by ultraviolet (UV) exposure from the sun. To reduce the risk of developing cancer from UV exposure, individuals are recommended to reduce sun exposure, seek shade, and use sunscreen when able.
- Practicing safe sex
Research shows that the human papillomavirus, or HPV, is also a risk factor for head and neck cancer. HPV is a sexually transmitted infection that can cause both cervical cancer and head and neck cancer. While there is a vaccine recommended to protect against the strand of HPV that is linked to cervical cancer, currently there is not a vaccine proven to protect against the variation that causes head and neck cancer. Experts recommend that individuals practice safe sex, including oral sex.
Detection and Treatment
Most types of head and neck cancers can be cured, especially if found early enough. While there are no current screening methods in place, people who regularly use tobacco and/or alcohol should receive general health screenings at least once a year. Regular health appointments provide medical professionals the opportunity to monitor for any abnormalities in the head and neck region. The most common symptom of head and neck cancer is swelling or a sore that does not heal. If someone at an increased risk of head and neck cancer experiences this, or any other persistent and unusual discomforts in the head and neck region, they should consult their doctor immediately.
The most common form of treatment for head and neck cancer is surgery. During surgery, the goal is to remove the cancerous tumor and some surrounding healthy tissue without impacting function. Like many cancers, it is sometimes impossible to completely remove the tumor. In cases such as this, surgeries may be paired with radiation therapy or chemotherapy.
For more information on head and neck cancer, please visit the National Foundation for Cancer Research.
A world without cancer is possible. Help us turn lab breakthroughs into life-saving realities.

5.7 Million+
Donors who have fueled NFCR’s mission

$420 Million+
Invested in high-impact research & programs
36+ Labs & Hundreds of
Nobel Laureates & Key Scientists received NFCR funding, driving breakthrough research